Survival bunkers and bomb shelters need reliable electricity sources to be fully functional. If a disaster strikes and everyone has to live there for a while, the right electrical system could save their lives. How do bunkers generate electricity? What options do they have? Here are the main sources that people can choose from — plus the pros and cons.
Generators
Generators are the most common sources of electricity for bunkers and any other power outage situation. The entire mechanism can go underground, which makes it easy to operate and maintain. They also come in various sizes based on how much wattage the building requires, which allows them to fit seamlessly into any home.
This power source converts mechanical energy into electrical charges that flow through an external circuit. The circuit includes a series of insulated wire coils that form a cylinder surrounding an electromagnetic shaft called a rotor. Turning the rotor causes the electrical current to flow through the coils, out of the generator and into electronic devices.
Generators can be stationary or portable, depending on the home’s needs. Stationary generators are bigger and have greater power outputs but are also expensive and more challenging to maintain. Some stationary generators can output as much as 5,000 kilowatts of electricity or more, though an average home won’t need more than 20 on the high end. Portable generators are smaller and more damage-prone, but their mobility gives them a huge advantage in survival situations.
Although generators are most people’s go-to alternatives when the power goes out, they have some challenges to overcome. The biggest problem is constant fuel consumption. Most generators can run for six to eight hours on a full tank, which means they need massive fuel stockpiles to be viable for an extended period.
Generators can run on different fuel sources, each with its advantages and disadvantages:
- Propane: Propane is the cleanest and most widely available fuel for generators, which makes it easy to create a large cache.
- Gasoline: Gasoline provides a higher power output and easier refueling options, but high prices make it challenging to stockpile large amounts.
- Diesel: Diesel is the safest fuel option because it has a longer shelf life and is less combustible than propane or gasoline.
- Biofuel: Some people make their own biofuels at home, such as biodiesel and hydrotreated vegetable oil (HVO), but these fuels require a generator conversion.
The other challenge of using a generator is dealing with the noise and exhaust fumes from the engine. Fortunately, there is a sweeping solution to both problems — store the generator inside an isolated room with exhaust venting and sound protection so it doesn’t impact other parts of the bunker.
Despite the noise, pollution and constant need for fuel, generators are still the best options for clean electricity. They have the longest track record of dependability, can last up to 15 years with proper maintenance and are available in countless models. There’s a perfect generator setup for any living situation, including the most advanced survival bunkers.
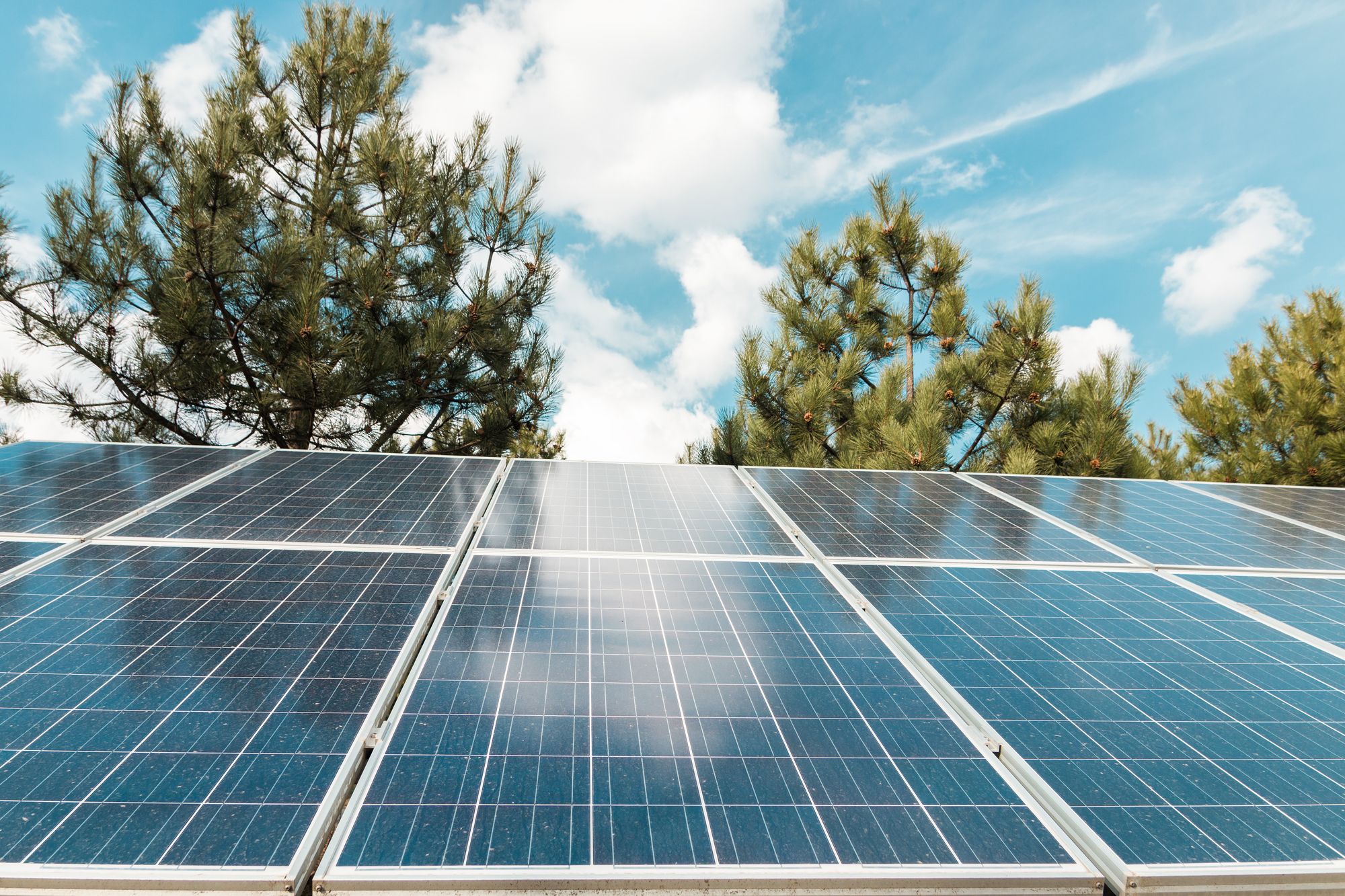
Solar Power
Solar power is the second-most popular electricity source for bunkers. This alternative is ideal for off-the-grid living as the nation’s power grid deteriorates. The components of a solar power system are much simpler than a generator — photovoltaic panels, charge controller, batteries and power inverter are the four major parts.
The panels are made of semiconductor materials, primarily silicon. They stay aboveground and absorb sunlight to create a clean electric current. The current moves from the panels into the power inverter, which converts it into alternating-current electricity for the home’s appliances. The charge controller prevents harm to the battery from overcharging.
Solar panels are typically cleaner, cheaper and more sustainable than generators. They also allow people to achieve complete energy independence, which might be the deciding factor when choosing a power source for a survival bunker. However, there are still some disadvantages to consider.
Despite their efficiency, solar panel installation and storage can be extremely expensive due to the price of raw materials. The average homeowner pays between $15,000 and $20,000 just to get the system running. However, they can slowly make that money back thanks to lower maintenance costs and electricity bills.
Solar power is also weather-dependent. The system won’t have the same energy output on cloudy and rainy days, which poses a huge problem in survival situations. Bunkers that rely on solar panels could be without electricity during extreme weather events. Other SHTF scenarios, like a nuclear winter, would also render solar panels useless.
Although solar panels provide cleaner electricity and lower operating costs than power generators, they are less reliable for emergencies. Both are great options in their own right, but generators still have a slight edge because of their reliability in any conditions.
Wind Power
Wind power is another renewable energy source that bunkers can use to generate electricity. The setup is similar to solar panels, with wind turbines installed aboveground and the rest of the system underground. The turbine blades collect the wind’s kinetic energy, and a connected drive shaft turns a generator to produce electricity.
The advantages and disadvantages of wind power are much the same as solar panels. They can provide clean electricity and low operating costs, but installation and storage are expensive due to the numerous heavy metal components. Their performance also varies with the weather because they rely on strong winds to produce high amounts of electricity.
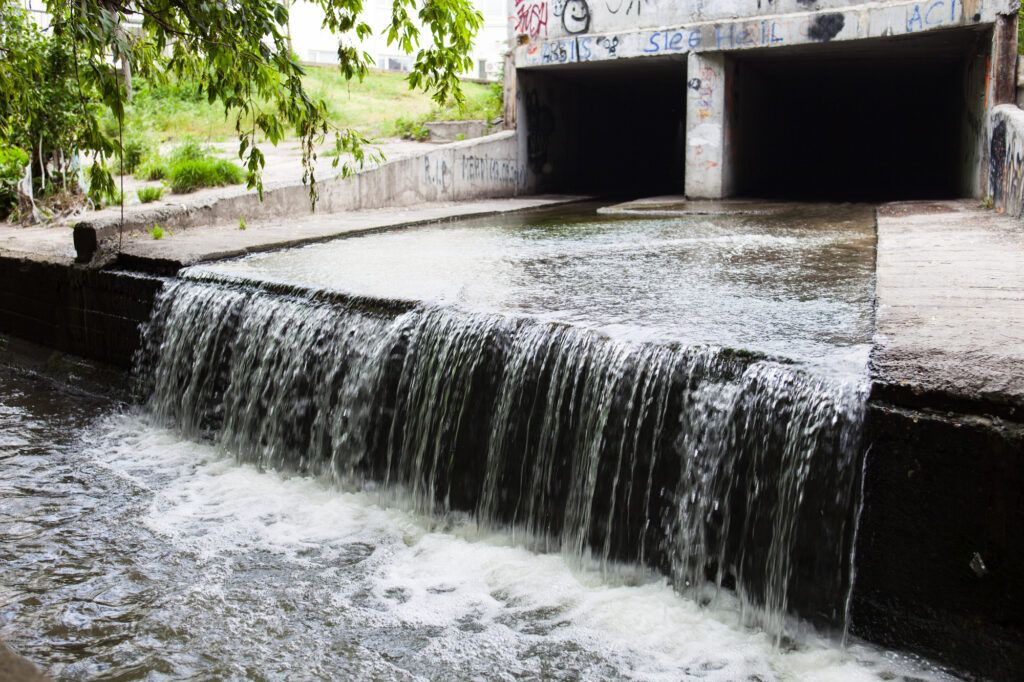
Hydropower
Hydropower creates electricity from the kinetic energy of moving water instead of wind. Water flows through the system’s piping and turns a turbine’s blades, which causes the generator to produce electricity. It pairs well with solar and wind power to help buildings meet their peak electricity demands.
The disadvantages of hydropower are the same as wind and solar — high upfront costs and a dependence on the local environment. If the bunker lacks available water reservoirs, then the system is useless. There must be a reliable year-round water source for hydropower systems to be financially and energetically viable.
Pedal Power
The last interesting method for generating electricity in a bunker is pedal power. As the name suggests, someone pedals a bicycle generator to create electricity through raw kinetic energy. It seems like a straightforward solution compared to other power sources, but pedal power is less popular for a reason.
The amount of labor required to provide consistent electricity is too much for most people to handle, especially if they’re living in a bunker. It’s vital to save calories in a survival situation, not burn them. Since generating electricity is so challenging, the system becomes inefficient and the costs outweigh the benefits.
Pedal power systems can also weigh up to 180 pounds, making installing them challenging. However, custom-engineered bunkers with flexible design plans address all these issues by including greenhouse rooms and larger living areas. It’s not the best solution but it can work in the right living situation.
Bunker Owners Have Options
Bunker owners have options when it comes to electricity. Generators and solar panels are the most common solutions, but wind power, hydropower and even pedal power are possible alternatives. People must stay flexible with their design plans to implement any of these power sources if necessary.





Get involved!
Comments